Bluez A2DP AudioSink for ALSA
Ok, here is the promised follow up for my previous post.I call it A2DP AudioSink for ALSA because at the moment that's all it can handle (which means it will not support HFP devices such as handsfree headset etc). That would not be necessary anyway because the existing ALSA PCM plugin (if you run bluez in socket mode) already supports bi-directional streaming with these devices. It is A2DP which is a problem.
Despite my rants about the quality of bluez DBus API documentation, it is actually quite complete and thorough when it comes to listing the available functions and their parameters. So I will not repeat that information here; I suggest that you download bluez 4.101 source tarball and look at its /doc directory, particularly audio.txt and media.txt (you can look at it online too here).
Instead, I will summarise the critical missing information that is necessary for your to build your own A2DP Sink/Source.
Let's start with the sequence of events that happens from the time of application startup, device connection and disconnection, until application shutdown. Instead of "A2DP AudioSink for ALSA" which is a mouthful, I will just call it as "your application" (or "your app", or even "you" for short) - I'm assuming here that you're reading this because you want to do your own stuff. Otherwise why bother, right?
Ok, here we go.
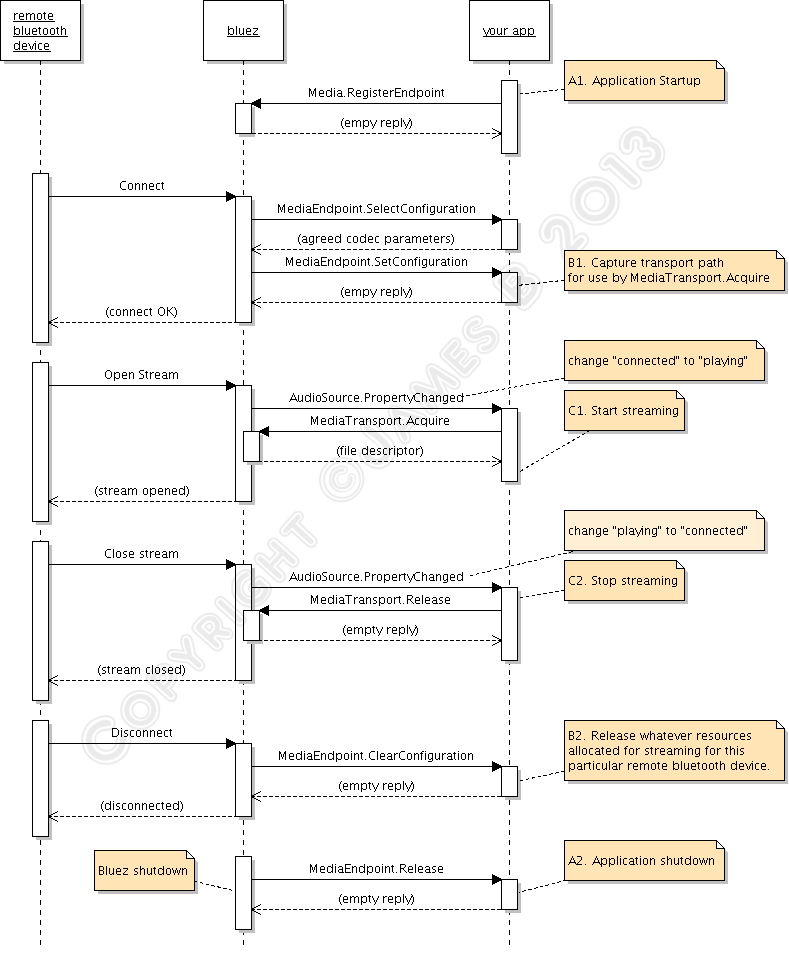
First, the caveat: the "bluetooth device" <--> "bluez" part of that diagram must be taken with a grain of salt, as it is not accurate. If you want to know the details you need to consult A2DP and GAVPD specifications. It's there so that you can see the big picture of what is happening.
You can see that there are 3 levels of events that happen during the lifetime of the your app. I have marked these as A, B, and C. Level A are the highest level events, these are startup/shutdown events and activities. Level B are events and actions that you must do when a remote bluetooth device is connected or disconnected. Level C are the actions you must do to carry out the actual audio streaming.
"Level A" events/actions (A1 and A2)
There are the events/actions you must do/handle when your application is starting up or shutting down. These actions/events only need to done once.
A1. Application Startup. Upon starting up, you need to tell bluez that your app will handle A2DP Sink or Sources for it. You do it by calling org.bluez.Media.RegisterEvent with the appropriate parameters, mainly UUID, Codec, and Capabilities. Bluez documentation doesn't make it clear, but you cannot just plug arbitrary made-up values here. "UUID" must be one of the pre-defined "Service Class identifiers" (from here), you want either AudioSource or AudioSink UUID. "Codec" must be one of the available supported codecs from A2DP specification, and the "Capabilities" must be filled with the particular codec's capabilities that you want to support.
If the registration is successful, you'll get an empty reply otherwise you'll get an error.
A2. Application Termination. Assuming you have successfully registered, bluez will notify you that your registration has been cancelled. This usually only happens the the bluetooth daemon itself is about to shutdown. Bluez does it by calling org.bluez.MediaEndpoint.Release method, which you must implement and handle (don't you wish now that bluez documentation differentiates between real "API" calls and "callback" interfaces, like this one?
 ). At this stage you don't need to de-register or do any other cleanup with bluez, you just need to clean-up your own resources. Reply with a blank message, and after that you are free to terminate your app.
). At this stage you don't need to de-register or do any other cleanup with bluez, you just need to clean-up your own resources. Reply with a blank message, and after that you are free to terminate your app.
"Level B" events/actions (B1 and B2)
There are the events/actions that happen / you must do when remote bluetooth devices get connected. It can happen multiple times within the lifetime or your app (ie between Level A events), for the same devices (in pairs), and for different devices (may be overlapping).
B1. Device Connection Events happen when a remote bluetooth device is connected. Assuming that your registration is successful, bluez will call your app again when an A2DP device is trying to connect to the computer. It does it using org.bluez.MediaEndpoint.SelectConfiguration. You will need to implement this method and interface and handle the call. Through this call, bluez will pass you some "Capabilities" codec parameters from the other end. You are supposed to compare this with your own capabilities and choose the best match that provide the highest quality audio. Your reply to bluez will contain the this chosen configuration.
If everything is all right, bluez will then call your app again, using org.bluez.MediaEndpoint.SetConfiguration. The parameter to this call should contain exactly the same codec parameters you gave back earlier in your reply to "SelectConfiguration". Among other things, the most important thing you must do here is this: you must record the "transport path" given as parameter of this call. It is a unique object path that you need to pass along to org.bluez.MediaTransport.Acquire to get the file descriptor you need to use for the actual streaming. If you don't keep that path, you can't find it again. All being good, you reply with empty message.
B2. Device Disconnection Events happen the remote bluetooth device is disconnected. Bluez will call you on org.bluez.MediaEndpoint.ClearConfiguration method. You are supposed to clear any of your resources you keep for that particular bluetooth device connection (ie, that particular "transport path"). Reply with a blank message.
"Level C" events/actions (C1 and C2)
These are the events/actions that happen / you must do to do the actual audio streaming. It can happen multiple times within "Level B" events for the same remote device, usually in pairs.
C1. Start streaming event. To detect this event, you must listen to org.bluez.AudioSource.PropertyChanged signal and keep track of its "State" property. The "start streaming" event happens when the state changes from "connected" to "playing". (There are a few other events too, which may be interesting for other purposes but not for us).
When this happens, you need to call org.bluez.MediaTransport.Acquire. Bluez will give you a file descriptor that you can read from, as well as its Read MTU (maximum transfer unit) - which is how big each packet would be. From here onwards, you can read this descriptor to obtain the A2DP packet, decode it, and output it. The Read MTU helps to determine how big a buffer you need to allocate. Note that the read isn't always successful, you must allow for error conditions such as EAGAIN because your CPU will be much faster at reading than what bluetooth (and the remote device) can send.
C2. Stop streaming event. Like "start streaming event", you can't decide this from org.bluez.AudioSource.PropertyChanged signal alone; you need to detect the transition, which is "playing" to "connected". When this happens, you need to call org.bluez.MediaTransport.Release to release the transport back to bluez. In my tests, this is not strictly necessary but it is the polite way of doing it. It is also good for you to detect this event so that you can can tell our "streaming" function to stop its work and rest for a while.
That's it! Easy peasy eh?
How about A2DP Source?
The events described above are to for you to make your computer act as A2DP Sink (or "Source", in bluez' parlance). What about building A2DP Source (the computer to send audio data to bluetooth speakers)? As it turns out, the sequence of events is exactly the same with very minor change:
1. Instead of AudioSource.PropertyChange, you need to listen to AudioSink.PropertyChange.
2. The transition you need to detect is a bit different - instead of "connected" -> "playing" (and vice versa), you listen to "disconnected" -> "connected" (and vice versa).
3. You write to the descriptor with encoded data instead of reading from it.
About The code
In the source, I create a thread for doing the actual streaming (reading/writing to the file descriptors). I create the thread when I received B1 event (SetConfiguration) but they are suspended until I receive C1 event - that is, after I have completed MediaTransport.Acquire call to get the file descriptor. I suspend the thread again when I receive C2 event, and only when I receive B2 event (ClearConfiguration) I terminate the thread.
The rest is straightforward. The code implements both Sink and Source. As you can see, the difference in handling is minimal.
The code is provided as an illustration and working example. It skimps on error checking; it focuses neither on performance nor robustness, but more on the working (and hopefully correct) way of handling A2DP connection under bluez. That being said, I find that the Sink is good enough, while the Source is a bit unsatisfactory. There is a README inside the tarball that shows how you can setup ALSA asoundrc for use with the A2DP Source so that it can act as a poor man's ALSA PCM plugin.
As usual, the code is released under GNU GPL Version 3 or later unless the bits that I took from PulseAudion and bluez itself (SBC stuff, SBC setup stuff, and actual A2DP packet encoding/decoding) - they are licensed as per the original PulseAudio and bluez licenses.
Get it from here.
Bluez 5 and beyond
Question: Bluez 4.x is already obsolete by now. What do I have to do to get this example to work with bluez 5?
Answer: A lot of work.
 I have not investigated bluez 5 version of this fully as I'm quite satisfied with bluez 4 for now. But from what I have gathered, the sequence of events is identical. Sure the DBus interfaces change their names (bluez 5 add "1" to the interface names, e.g. "org.bluez.MediaEndpoint" becomes "org.bluez.MediaEndpoint1"); and the signals change their skins too (AudioSource/AudioSink are gone, replaced by generic org.freedesktop.Properties.PropertyChanged, and you can probably decide whether to start/stop streaming directly from the state instead of having to watch the transitions), but the underlying events are still the same.
I have not investigated bluez 5 version of this fully as I'm quite satisfied with bluez 4 for now. But from what I have gathered, the sequence of events is identical. Sure the DBus interfaces change their names (bluez 5 add "1" to the interface names, e.g. "org.bluez.MediaEndpoint" becomes "org.bluez.MediaEndpoint1"); and the signals change their skins too (AudioSource/AudioSink are gone, replaced by generic org.freedesktop.Properties.PropertyChanged, and you can probably decide whether to start/stop streaming directly from the state instead of having to watch the transitions), but the underlying events are still the same.
Conclusion
A2DP is just a small part of Bluetooth specification. If you look at the links I gave earlier, you will see Bluetooth comes with over two dozen "profiles" (ie, functionalities). Bluez doesn't implement all of them (although the unimplemented list is getting smaller very day, thanks for the very hard work of bluez developers), which is fine, but bluez could really do better with its documentation. At least give us userspace programmers something to get around our head on. Until that happens, I still consider that "bluez is one of the best kept secrets in Linux".
Comments - Edit - Delete
Bluez must be one of the best kept secrets in Linux
PrologueYou don't believe me? Quick - tell me, what does Socket option mean in /etc/bluetooth/audio.conf? Why does it have to be enabled for audio streaming (from computer to bluetooth speakers/headsts) to work? Along the way, what are other options (other than this "Socket") available, and what do they mean?
Not in your local manpages? Here, let me google it for you: http://bit.ly/11q1jdq
The first link (at least in my browser here, everyone knows Google does habit-tracking...) will bring you to the ArchLinux wiki. Arch Wiki is usually very explanatory, but for this case, if you scroll down and read the details about this "socket" stuff - well, it simply refers back to its source, Gentoo Wiki. Let me save your from googling http://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Bluetooth_Headset. Yup, no explanation there either.
And from there, it goes down the rabbit hole. And down there I went.
Down the rabbit hole
The latest release of Fatdog64 comes with partial bluetooth support using bluez 4.101 (the latest and probably final release of bluez 4.x series, now that is has been superseded by bluez 5.x). Bluez 4.x series comes with an ALSA PCM plugin. This plugin makes it possible for the computer to stream audio to bluetooth speakers (and headsets) - provided, of course, one has the correct settings in audio.conf with that Enable=Socket line inside (yes, Fatdog64 is pre-configured with this). All that is required after that is to setup the correct asoundrc file, and in Fatdog64 this is taken care of by the Set Default Soundcard applet in Fatdog64's control panel. In short, with this you can listen to youtube using your bluetooth speakers.
In technical terms, the bluez ALSA PCM plugin is a Source - source of the audio stream, to be sent over to the bluetooth speakers. The speakers in this case is called as the Sink - where the audio stream is received.
But there is no plugin for the reverse.
That is, how to to listen to the music in your phone from your computer? (the computer may be connected to a stereo set). That is, how to make the computer as the Sink with the phone as the "Source"?
Back to google. And google I did, nothing I found. All the references I can find when I googled for "bluetooth streaming audio to my computer" always refer to how to do it with PulseAudio (load pulseaudio module this and module that, connect them, and magic happens). Very helpful and very handy except that it is useless for me because I don't run PulseAudio and I'm not about to. (I don't have to run PulseAudio or any other audio server when I plug-in a USB audio soundcard - so why should bluetooth?!)
Remember what I said at the beginning? "Bluez must be one of the best kept secrets in Linux."
Bluez source tarball comes with a /doc directory that contains a handful of text files containing extremely concise DBus "API" descriptions. Now, I am not allergic to documentation in text format (in fact I'm very annoyed with packages whose documentation need to be "made" or "built" first before it can be read - especially if it requires huge or esoteric tools to do so - but that's another story); but did I just say "handful" and "extremely concise"? You can have a taste of this "documentation" here. No howtos. No tutorials. Not on the source tarball, not on bluez.org, not anywhere. In fact, later on I learnt that some of these "API" are not APIs at all - some of them are "function prototypes" ("DBus interfaces") for callbacks which our own application has to provide and will be called by bluez! (instead of us calling into bluez). (Note: There is actually a rather nice bluetooth/bluez tutorial here, but it focuses on data communication aspect of bluez using sockets and RFCOMM; nothing to with bluez DBus API and audio/media. Again, there is no documentation from bluez for these subjects too!).
Sure, hotshot - someone might say - why don't I just read pcm_bluetooth.c (the ALSA PCM plugin) from bluez package, understand the interface, and reverse it to create the "Sink" interface? I will have to admit, I'm not that well versed with ALSA plugin interfaces which is absolutely required if you want to separate the ALSA stuff from bluez stuff in pcm_bluetooth.c (I know ALSA good enough to output sound using its API, but that's it). And my original idea is once I have the "Sink" interface, I will extract the audio stream in a known format and send it to stdout where I can pipe it over to "aplay" or "ffmpeg" or "sox" or whatever to actually output the soud; this way I don't have to mess with ALSA libs at all.
So I didn't follow that path, and later on it turned out to be a good move for a reason even more obscure: The ALSA PCM plugin talks to bluez using what is called as the "audio socket API" (this, by the way, is the answer to the first question on the opening paragraph of this post) and it is already deprecated for sometime (which is why it isn't enabled by default).
OK. Lacking this first-hand information from bluez, I spent hours googling to find explanations or at least overview of what this bluez DBus audio/media API is all about.
Among hundreds of results from Google, I could only find one place that explains it, here. It is simply the simplest, clearest overview of bluez usage from userspace perspective. It was written in the context of Android but it easily applies to other situations too. Buried deep in that post, is a link to a PDF document which highlights bluez DBus API overview, http://download.tizen.org/misc/media/conference2012/wednesday/bayview/2012-05-09-0900-0940-bluez-_plugging_the_unpluggable.pdf.
One wonders why this very important document is hidden deep inside Tizen's website maze. Only after one realises that bluez is mainly driven by Intel (and Nokia in the past, when they were still supporting the Maemo platform), you will see the connection: Tizen is a joint Intel-Nokia initiative too (being the rightful descendant of Maemo/Meego/Moblin). There is nothing wrong with that, in fact I'm glad that they take the initiative to sponsor the development of this very important protocol stack in Linux kernel. My only question is this: why oh why isn't this information available from bluez.org instead; is that too much to ask?
Anyway. That PDF got me started, but that information is - as mathematicians call it - necessary but not sufficient.
One need to read this post (I need to enable the Source interface in audio.conf), this post (when I can request bluez for the file descriptor for actual reading/writing of audio data) and then lastly this post (I need to disable the Socket interface otherwise the bluez Media DBus API won't work!) to make it work.
Once done this enabled me to dump the audio data to stdout.
Nice! But how to actually listen to that?
As it turns out, the audio data is compressed with SBC codec. But I can't just use "sbcdec" tool from SBC package to decode it, as the audio data is encapsulated in A2DP packets, not naked SBC-compressed audio data. A2DP packets are RTP packets (referenced by A2DP specification, and detailed in this IETF draft) containing A2DP Media Payload. We need to extract the SBC audio data, pass it through SBC decompressor, and only then we get raw audio data that can be sent to ALSA.
I took a shortcut - I already know of a good implementation that can do this decoding: PulseAudio. So I cracked open PulseAudio source tarball. Fortunately the encoding/ decoding functions are obvious enough even for one who knows zilch about PulseAudio internals; I took the decoding function out and merge it to my code.
Minor details such as how to tell my phone to connect its audio source to my computer was found rather quickly by trial and error, like this:
dbus-send --system --dest=org.bluez /org/bluez/[bluetoothd-pid]/hci0/dev_XX_XX_XX_XX_XX_XX org.bluez.AudioSource.Connect(it is one long line, not two lines).
And the first sound that came from my phone aptly came from a song called "Painting Raindows" :)
Notes: Bluez sinks and sources
Note to self: bluez' treatment of the terms "Source" and "Sink" are not consistent. Let me explain:
Bluez audio has two interfaces, like these:
"bluetooth device <--> (a) bluez (b) <--> application"
For example, in our case, viewed from (a), the interface is called as a "sink" because bluez receives data from external bluetooth device (the phone). Once processed, bluez will pass the data to an external application (view (b)); viewed from here bluez acts as a "source" of data to this external application.
The Bluetooth specification always uses viewpoint from (a). Bluez uses both view points, sometimes from (a) and sometimes from (b). That is also the very reason why to enable the computer to act as an audio "sink", we need to add "Source" to audio.conf.
Did I say that bluez must be one of the best kept secrets in Linux?
One more thing, honey ...
Once I got the audio sink working, I was about to wrap up and close my little experiment when I realised something.
Do you remember what I said about enabling Socket in audio.conf to enable ALSA PCM plugin, so that one can stream audio from the computer to the external bluetooth speaker? Good. Do you remember what I said about disabling Socket in audio.conf before the bluez Media DBus API can work, so that we can stream audio from phones to the computer? Good.
Not!
Obviously it means I can't do both at the same time!
Well, the solution, according to the bluez team, is simply to drop the Socket API (and the associated built-in ALSA PCM plugin) altogether because it is already deprecated and will be removed soon anyway! In another words, I will now also need to write the an A2DP "Source" interface. This time around, google didn't help me at all, but fortunately the bluez team did the correct thing and followed the same exact event flow with the "Sink" interface, as tests and trials confirmed. So I just need to modify the code a little to listen to different events (AudioSink instead of AudioSource). As before, the A2DP packet preparation and SBC compression is taken from PulseAudio.
To the future and beyond ...
And the happy ending is, all this work will be at least partially wasted in bluez 5. Firstly, bluez 5 removes the Audio Socket API (which also means the built-in ALSA PCM plugin is gone for good). Secondly, bluez has big API changes. Apps built for bluez 4 *will not work* without re-factoring and re-testing. Sure, using the DBus API instead of the socket API is a smart move, but still not good enough for bluez 5.
I am not the only one. It is telling that even PulseAudio team themselves have not released a version that supports bluez 5, six months after the first version of bluez 5 was released. Mind you, PulseAudio team works closely with bluez team; they got first hand knowledge of the impending changes and has already started to patch PulseAudio to accomodate bluez 5 API well before bluez 5 was officially released....
Apparently, despite being the official Linux bluetooth stack since 2001, bluez userspace API is not stable yet...
As for Fatdog64, I think I will stick with 4.101 for a while.
The code
I will follow this up with another post that documents all the findings in more details, as well as the corresponding source tarball.
The Sink works relatively well, the Source, while usable, isn't a comparable replacement for the ALSA PCM plugin. It sort of works; you can pipe raw sound data to it and you will hear it on your bluetooth speaker. Combined with ALSA PCM File plugin, it can be used as a poor man's ALSA PCM output plugin, but it doesn't always work (ffmpeg works, VLC stutters, youtube simply crashes). It also suffers from an odd problem of stuttering when I connect both the sink and source at the same time (the sink never stutters).
The code is meant as a proof-of-concept, as a learning tool, and as a working example of the bluez Audio/Media interfaces. It focuses on neither performance nor robustness. If I have time and inclination I may do one that do it properly - as a native ALSA PCM plugin.
Epilogue
I have not talked about DBus, bluez' IPC of choice. One can't avoid DBus at all because bluez API is exposed as DBus method calls (bluez has other kind of APIs - these are totally undocumented). Some jokingly said that one of the reason why DBus is so popular in embedded devices is because if people want to get bluetooth functionality using bluez, they'd better bring DBus in too ...
I'd talk about DBus, "whose reference library is not meant to be used", in another occasion.

As a parting note, here is the link to a suite of bluetooth userspace tools much better than the one you can find in bluez package itself. I wish this tool is more popular, I wish I had know this tool when I started to experiment with Fatdog64's bluetooth support. Isn't it telling that most of wikis and solution websites advocate the usage of "simple-agent" python script when one needs to do device pairing on command line - when this python script actually lives in "/test" directory inside bluez source tarball? Hmmmm.
Bluez must be one of the best kept secrets in Linux.
Comments - Edit - Delete